
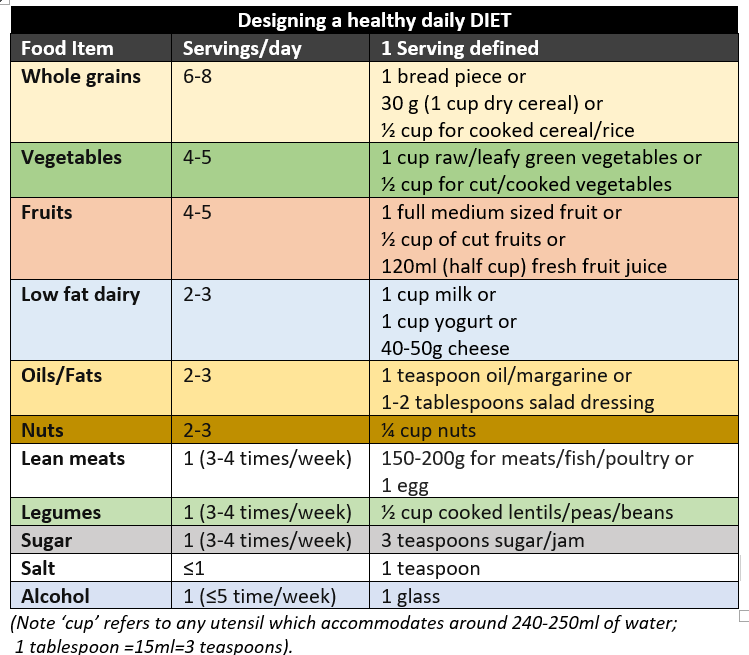
Here is a guide to help you design your daily healthy diet.
Eating a daily diet on these lines helps control blood pressure and cholesterol, lowers the risk of heart problems and diabetes, maintains appropriate BMI and weight, and also helps in long-term good health, energy levels, and wellness.
One should select food items from below, calculate the amounts according to servings, and distribute the same across three principle meals (breakfast, lunch, dinner), and two snacks (mid-morning and mid-evening) daily.


A healthy diet should be complemented with good sleep (8 hours on most nights) and regular exercise (at least for 30-45 minutes, 5 times/week).
Caloric intake
The recommended daily calorie intake ranges from 1500-2500 calories based on gender, age, height-weight, and physical activity. It is higher for people with more physical activity, or those who exercise or weight train regularly. If wanting weight loss at an average rate of half a kg per week, a reduction by 500 calories per day can be kept as a target.
Around 55-60% of calories should come from carbohydrates, 10-15% from proteins, and the rest from fats (with saturated or trans fat being <10% of total calories). While carbohydrates and proteins yield 4 calories/g, fats yield 9 calories/g. The daily intake recommended for at least 1500 calories is therefore around 200-250g carbohydrates, 50g proteins, and 40-50g fat.
[Note: In the context of nutrition, the terms Kcal (kilocalories) and calories are used interchangeably and are considered the same.]
Carbohydrates
They are the main sources of energy for the body. Sugars like sucrose (from common sugar), fructose (from fruits), lactose (from milk), and maltose (from starch) are all broken down to glucose by digestion. Glucose is used by our cells to give energy that is stored in packets called ATP. Glucose is stored in our body as glycogen in the liver and muscles. Cereals, pulses, common sugar, some vegetables (like potatoes and beets), and some fruits (like bananas, apples, mango, and grapes) are the main source of carbohydrates in our diet.
Carbohydrates are also sources of fiber in our diet. If the amount of fiber is high in the food item being consumed, the net carbohydrate caloric value is considered that much lower, and one needs less quantity to feel full. The fiber can be soluble or insoluble. Insoluble fibers add bulk while soluble fibers absorb water, and these actions aid the smooth and efficient passage of stool thereby preventing constipation.
Brown rice and whole wheat have good insoluble fiber. Fruits and vegetables are important sources of soluble fiber. Green vegetables and fruits like berries, citrus fruits (lemons, oranges), peaches, papaya, pineapple, watermelon, and kiwi, have good fiber content and are low in net carbohydrates. Pulses, in addition to providing carbohydrates, are also good sources of proteins and fiber.
The approximate amount of net carbohydrate in common daily items is as follows-
- 100g cooked rice (white/brown): 45-50g
- 1 wheat chapati/ 1 slice of bread: 13-15g
- 1 potato (medium): 30g
- 100g cooked pulses (dal): 20-25g
- 100g roasted mixed nuts (approx. 100 nuts): 30g
- 1 banana/1 apple/ 1 mango/ a cup of grapes: 25g
- 1 teaspoon sugar: 4g
- 1 large pizza slice/ 1 ready noodle pack / 1 doughnut: 45-50g (equivalent to 2-3 regular-sized biscuits)
Proteins
Proteins help in growth, repair, muscle building, and immunity, along with being a reserve source of energy. Animal sources of foods are rich in proteins, while among vegetarian sources, some dairy items, soy, nuts, and pulses have good amounts of proteins.
Certain stages in life require higher protein in diet like during growth and development, high physical activity, illness, convalescence (recovery phase), pregnancy-lactation, and in the elderly. A diet higher in protein and lower in carbohydrates can help in weight loss and improve control or reduce the risk of lifestyle diseases like diabetes, CVD, PCOS, and hypertension.
Some fruits are rich in proteins like guava, kiwi, cherries, avocado, apricots, jackfruit, and resins.
The approximate amount of protein in common daily items is as follows-
- 100g soy chunks: 50g
- 1 boiled egg: 6g
- 100g chicken/meat/fish: 25-30g
- 100g cooked pulses: 10-15g
- 100g roasted mixed nuts (approx. 100 nuts): 18-20g
- 100g cheese/cheddar: 25g
- 100g tofu/paneer: 15-20g
- Milk 100ml: 3g
Fats
Fats are sources of reserve energy and also part of the components of the cell membranes of our body tissues.
Oils and butter are the main sources of fat in the diet. Foods like butter, ghee, palm/coconut oils, cheese, and red meat (beef/pork/lamb) have high amounts of saturated fat, therefore are better taken sparingly. Unsaturated oils include poly and mono unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA and MUFA) like sunflower, safflower, sesame, rice bran, and olive oils. Walnuts and oils of fish, soy, canola, and flaxseed are rich in omega-3 PUFAs that have beneficial effects of reducing blood cholesterol and triglycerides, and having an anti-inflammatory effect.
Cooking oils, ghee, and butter have 4-5g of fat per teaspoon.
Nuts like cashews, walnuts, and almonds have about 40-50g fat/100g.
Understand fats in detail here.
Vitamins and Minerals
These are micronutrients so are required in very small quantities. In a diet containing adequate cereals, pulses, vegetables, and fruits, deficiencies of vitamins and minerals are rare.
Vitamin A is found in animal liver and dairy products while beta carotenes (converted to vitamin A by the body) are found in carrots, tomatoes, and green leafy vegetables (like spinach, lettuce, broccoli), pumpkins, and ripe mangoes. Vitamin A is important for vision (especially in the night/dark) and helps to maintain healthy skin and hair.
B group vitamins are available in cereals, pulses, green vegetables, nuts, yeast, and meats/fish. However, vitamin B12 is available only in animal sources like meat, egg, poultry, and fish, but for vegetarians, it can be obtained from dairy products. B group vitamins are required for general health, well-being, energy, metabolism, and many body processes. Vitamin B12, folic acid, and B6 play an important role in the formation of blood cells and in preventing anemia. Biotin is an important B group vitamin for healthy hair and nails.
Vitamin C is found in citrus fruits, berries, and fresh vegetables. It aids in immunity and keeping bones, gums, and blood vessels healthy.
Vitamin D is made by the body from cholesterol when exposed to sunlight. It is found in animal sources like eggs, fish, meat, and poultry. It helps in calcium absorption and bone formation. It has also been seen to improve immunity and general health, well-being, and energy levels.
Vitamin E is rich in vegetable oils, grains/cereals, and nuts. It helps in healthy skin and hair, and slowing down the wear and tear/aging of body tissues.
Vitamin K helps in blood clotting and is available in green vegetables, cereals, fish, meat, and eggs.
Vitamin A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble and therefore are absorbed only with oils and fats. Vitamin B and C are water-soluble. Vitamin A, C, and E are antioxidants (help slow down wear and tear/aging of body tissues, and aid regeneration/repair). Milk is a good source of fat-soluble vitamins, but not B and C.
Minerals are also needed by our body in minute quantities. Among minerals, iron and calcium have vital roles. Iron is found in green vegetables especially spinach, chicken, lean meat and egg yolk. It is the vital vitamin required for hemoglobin which carries oxygen in the red blood cells (RBCs). Calcium is found in milk and dairy products as well as green vegetables and sesame. It is vital for healthy bones and teeth. Other important minerals like zinc, magnesium, manganese, selenium, chromium, copper, etc. are obtained adequately from vegetables, pulses and cereals. Common salt is the main source of sodium, and is fortified with iodine which is crucial for thyroid function. Fruits are a good source of potassium.
Many common food items like milk, cereal, bread, flour and packaged foods are fortified with all vitamins and minerals.
IMPORTANT MEAL AND EATING HABITS
- Eat at regular times and do not have erractic eating schedules.
- Wash your hands before eating.
- Eat in proper erect posture, and avoid slouching lying down postures while eating.
- Allot proper time for your main meals, and avoid working, using the phone/laptop, reading or watching any screen during mealtime.
- Eat mindfully, registering and enjoying the taste of each food item.
- Avoid talking too much while eating.
- Do not gulp large boluses of food. Chew food thoroughly before swallowing.
- Avoid heavy exercise or lying down immediately after eating.



Further reading –
Incorporating the DASH diet to reduce BP, BMI and Cardiovascular risk
Diabetes: Understanding health risks and effective diet-lifestyle measures

