Quick Read – Exercises to Reduce Snoring
SNORING
Snoring refers to loud, harsh noises during sleep. This happens due to the narrowing of the air passages of the nose, mouth and throat due to falling back of the tongue and relaxation of the throat muscles, seen during sleep especially while lying on one’s back.
SLEEP APNEA
Apnea refers to stopping to breathe. Hypopnea means abnormally shallow breathing while bradypnea means abnormally slow breathing.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs if the air passages of the throat, nose or mouth narrow down to such an extent during sleep that there are moments when breathing stops completely. The person makes grunting, gasping or choking loud sounds during these sleep apnea episodes. This helps the person momentarily wake up so that air passages open and breathing starts again, though the person may not realize or remember the same. These multiple episodes of apnea and waking during sleep prevent deep and restful continuous night sleep.
Snoring in sitting posture as seen in many plane/vehicle passengers is an indication of more airway obstruction and has an even higher risk for sleep apnea.
Central sleep apnea is rarer and occurs when the signals from the brain to breathing muscles during sleep are improper, as seen in some brain diseases like infections and stroke, or with some narcotic drugs.
Sleep-related hypoventilation refers to insufficient breathing (too slow-bradypnea or too shallow-hypopnea) during sleep that leads to decreased oxygen delivery and increased carbon dioxide in the blood.
Sleep apnea and sleep-related hypoventilation are together called sleep breathing disorders, or sometimes sleep apnea-hypopnea. ‘At home sleep apnea testing‘ is available for diagnosis and planning management.
PREDREDISPOSING FACTORS
Risk factors for snoring and sleep apnea may be present that need to be corrected. However, sometimes no cause may be found (idiopathic). The following are some of the factors which make a person more likely to snore or have sleep breathing disorders:
- Male gender and increasing age
- Alcohol intake in the late evening
- A late heavy meal/dinner
- Sleeping in dry environments or lack of hydration
- Obesity (more fat around the neck) or being overweight
- Smokers
- Certain medicines like muscle relaxants or antianxiety pills (benzodiazepine group) taken at bed-time
- Substance/narcotic abuse
- Nasal allergies
- Heavy cold
- Presence of outgrowths in the nose (called polyps)
- Swollen/enlarged turbinates (structures made of bone, blood vessels and tissue in the sidewall of the nose which help warm and moisten the air entering the nose)
- When the dividing bone of the nose is slanting (deviated nasal septum -DNS)
- Throat infections
- Presence of enlarged tonsils or adenoids (a common reason for snoring in children)
- Airway or lung diseases
- Emotional or behavioral conditions
- Neurological or muscular disorders
- Hormonal disturbances
- Genetic conditions
HEALTH EFFECTS
People who snore often have a feeling of tiredness in the morning as if they have not slept or rested enough. This may be accompanied by daytime sluggishness, sleepiness or irritability and inability to concentrate optimally. The feeling of dryness in the mouth and nose may also occur.
If sleep apnea or sleep-related hypoventilation is present, daytime sleepiness and tiredness are even more prominent along with impaired work performance and sometimes morning headaches. Loss of sexual drive may also occur.
Snoring with sleep apnea in the long term are risk factors for developing diabetes, weight gain, increased blood pressure, heart disease and stroke. Research is also showing now that sleep apnea can hasten the progression of fatty liver disease.
Therefore, from both short term and long-term health and wellness perspective, it is important to look for solutions to reduce and control snoring and sleep apnea.
HEALTH SOLUTIONS
Snoring can be reduced considerably by lifestyle solutions.
LIFESTYLE MEASURES
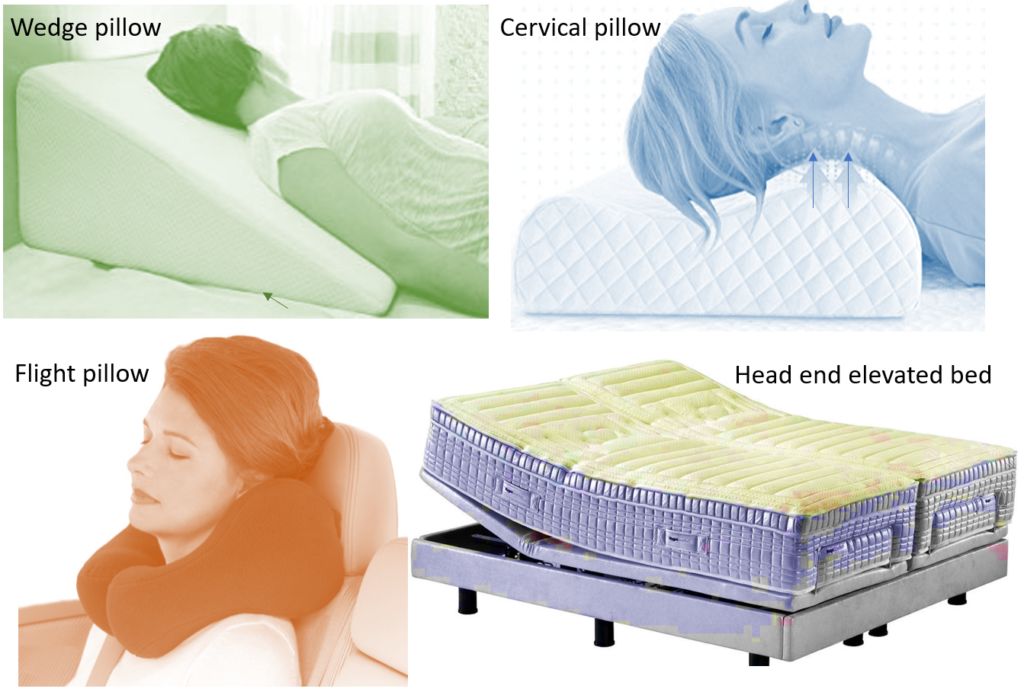
- Train to sleep on your side rather than on your back. Using an extra pillow to prop up the head or elevating head end of the bed can help. If you snore while sitting in flights/vehicles, avoid reclining.
- Avoid heavy meals and alcohol at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- If overweight, consult a nutritionist for a weight loss and exercise plan with a target reduction of at least 2-3 kgs to have an effect on reducing snoring.
- Avoid intake of muscle relaxants and antianxiety/sleeping pills (of the benzodiazepine group of medicines)
- Get a complete medical examination done to rule out the mentioned issues in the mouth, throat or nose.
- Treatment of nasal stuffiness due to nasal allergies or cold with decongesting medicines or nasal sprays can help reduce snoring.
- AC and closed dry environment (like seen in flights) can cause drying of air passages and increased tendency to snore. A humidifier spray or saline nasal spray can help. Have a few sips of water just before going to sleep.
- There is some research to suggest that smoking increases snoring risk therefore smokers are advised to restrict and give up the habit.
ANTI-SNORING EXERCISES
The aim of these exercises is to
- Increase the tone and strength of throat, tongue and palate muscles
- Keep air passages open at all times and reduce sleep apnea
Here are 5 exercises below. The HOLD TIME in each position is 5 seconds, and each exercise set is to be REPEATED 5 times.
So it is the 5-5-5 approach to reduce snoring.
- Tongue Stretch: Stick the tongue out of the mouth fully as much as possible, then move it to one side and then to the other side as much as possible without curling the tongue. Hold in each position for 5 seconds, and then put back in. Do this at least 5 times. (Each day try to stick out your tongue as much further as possible, and also try to touch the chin with it).
- Tongue Rolls: Press the tip of the tongue on the roof of the mouth, then move it as back then as front as possible on the roof of the mouth (palate). Repeat this back and forth motion 5 times. Then with the mouth closed, rotate the tongue inside clock wise 5 times, then anti clockwise 5 times.
- Jaw Stretch: Look at the ceiling, drop the lower jaw fully down, then raise it up slowly and firmly so that the lower lip overlaps the upper lip. Repeat 5 times. Then look straight, open the mouth wide (with tongue inside), move the lower jaw to one side, hold for 5 seconds, bring back and close. Then open wide again and move lower jaw to the other side, hold for 5 seconds, bring back and close mouth. Repeat this set of 3 exercises 5 times.
- Cheek Stretch: With your index finger in the mouth, push the cheek away from the teeth for 5 seconds then release. Do this on each side around 5 times each.
- Vocalization: Pronounce the 5 vowels for 5 seconds each, one by one with full mouth stretch possible for each particular vowel.


In all the above exercises, you will be able to feel a tension and stretch in your mouth, and throat. There are other exercises which may be recommended by trainers. Biting down a pen or a pencil for 5-10 minutes or until the jaw feels sore/tight, just before bedtime can help strengthen jaw muscles. One can also chew gum for 10-15 minutes before bedtime. Interestingly vocal music training is known to be helpful in preventing snoring!
Breathing techniques practiced regularly can also reduce snoring and sleep apnea, and enhance work capacity and productivity.
ANTI-SNORING PILLOWS
These help to keep the air passages open as shown below. Some of them now come with memory or microbead foam and are called ‘smart pillows’ as they adjust to the head size and neck curvature.


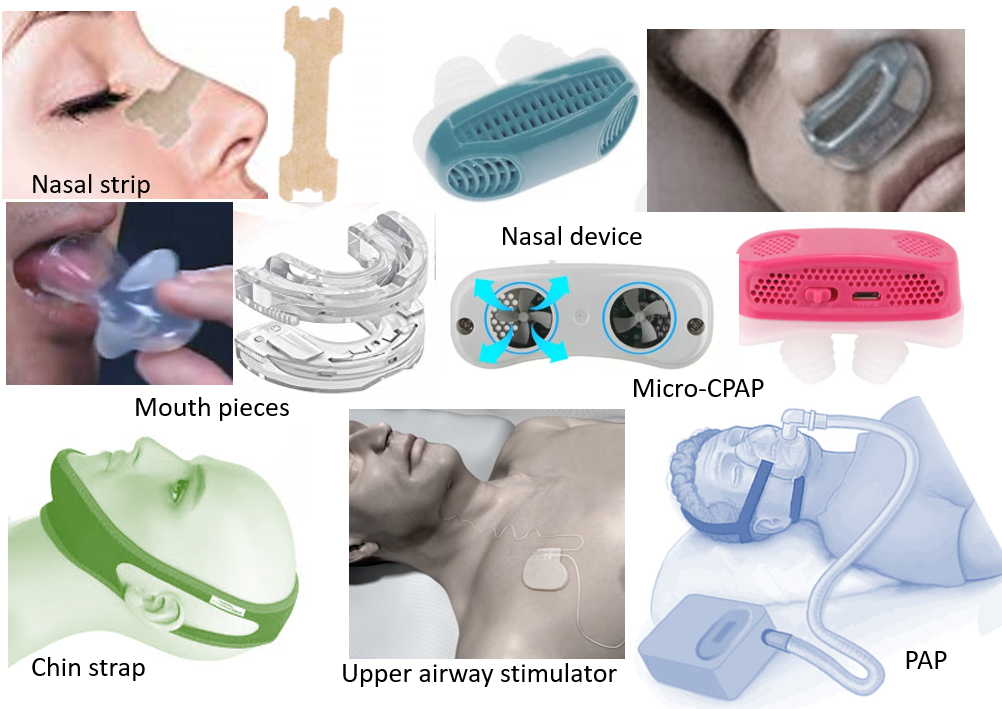
DEVICES
Nasal devices or strips help to keep nasal air passages open, and relieve nasal congestion.
Mouth devices help to keep mouth, tongue and palate in position to keep air passages open. These may include mandibular advancement devices that are specially designed mouthpieces to bring forward the jaw to facilitate the opening of the airway. Other mouth devices hold the tongue in place, avoiding closure of the airway by the falling back of the tongue.
Chin straps help by preventing jaw-dropping and thereby not letting the tongue fall backward.
It is important to note that the above devices may be useful in some but not others. Some of these devices in common terms are also called night guards for snoring. Therefore, it is best to go ahead with one of them after medical consultation and examination with a Physician, ENT specialist or Dentist.
SLEEP APNEA AND HYPOVENTILATION
In the case of sleep apnea, for an effective evaluation and diagnosis, it is important to consult a doctor who will conduct a general physical examination and recommend more detailed tests when needed. An ENT examination to rule out upper airway anatomical abnormalities is advised.
Polysomnography is a test that records brain waves and activity, different stages of sleep, blood oxygen levels, breathing, heart rate and leg movements during the sleep. It is usually performed in a sleep clinic but is sometimes also done in home setting. Thereafter further tests maybe advised like a CPAP titration to determine the right level of treatment.
Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) – This device is usually recommended for patients with prominent day time functioning impairment or high cardiac risk due to sleep apnea.
PAP uses a stream of high-pressure compressed air to keep the airway open and prevent its collapse and closure, which causes sleep apnea episodes.
The airstream in PAP can be :
- Constant and Continuous (CPAP- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure). Now micro-CPAP devices are available that combine a nasal device with blowing-in pressurized air to keep nasal passages open.
- Variable or Bilevel (VPAP/BiPAP). The airstream pressure is less when the patient breathes out as compared to breathing in. This is useful in patients with breathing problems and reduces breathing effort.
- Automatic (APAP) or Auto-CPAP. These machines have sensors for air pressure so as to adjust pressure rates according to the patient’s breathing pattern and airway resistance.


In all cases, underlying medical conditions or predisposing causes should be sought, diagnosed and treated. All devices mentioned are for patients with diagnosed sleep apnea and hypoventilation after evaluation through sleep tests and recommendation by an ENT specialist or pulmonologist.
PROCEDURES
Upper airway muscle stimulator is a device that monitors the breathing patterns while sleeping and based on that, delivers mild stimulation to the airway muscles to keeps the air passages open during sleep. It is mainly for patients who have snoring with obstructive sleep apnea. The upper airway stimulation system consists of a small impulse generator implanted beneath the collar bone with a tunneled breathing sensing lead placed between the external and intercostal muscles of the chest, and a tunneled stimulation lead attached to the branch of the hypoglossal nerve that produces tongue protrusion. When the sensing lead detects inspiration is occurring, the impulse generator sends a signal via the stimulation lead to the hypoglossal nerve, which results in slight forward displacement of the stiffened tongue. The impulse generator is similar in size and appearance to a cardiac pacemaker, and the latest version is MRI compatible.
Surgical correction of anatomical abnormalities of the nose, mouth or throat may be required sometimes to treat snoring or sleep apnea. These may include removal of enlarged tonsils or adenoids, correcting a deviated septum in the nose, removing a thickened nose turbinate or, removing excess tissue in the back of the throat. Other surgical procedures include stiffening of the palate and forward advancement of the tongue or jaw.
Read more on Sleep apnea test and Diagnosis: https://sleepingtest.com/
Also read –
Not getting enough sleep can be detrimental to health: Tackling Insomnia
For any query, additional information or to discuss any case, write to info@drvarsha.com and be assured of a response soon
References



